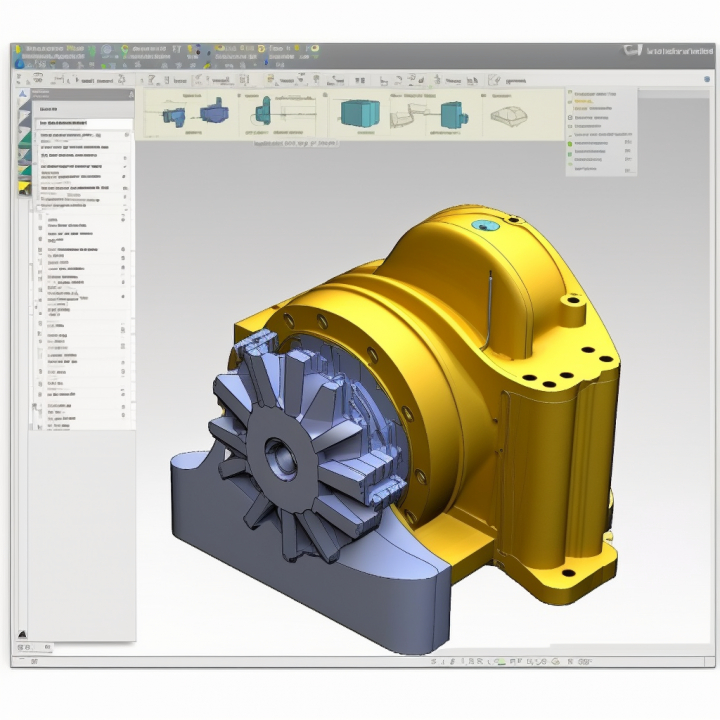
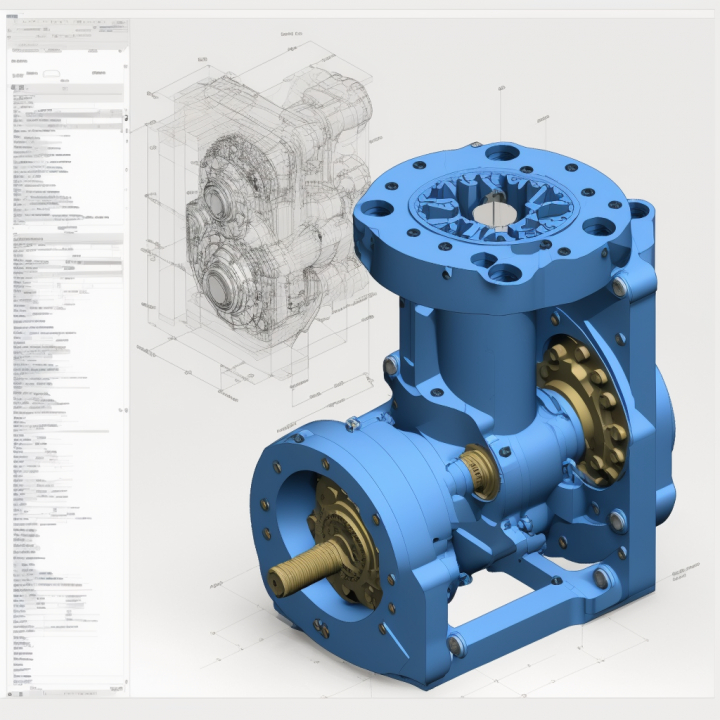
Solid Edge (2)
Optimized Solutions for Solid Edge
SimWise 4D stands as the most cost-efficient simulation tool integrated with Solid Edge. It enables bi-directional transfer of parts, assemblies, assembly relations, design variables, and dimensions from Solid Edge to SimWise. Once in SimWise, users can add simulation-specific information, resulting in a fully functional virtual prototype that allows a wide range of simulations to be executed using data from Solid Edge.
Should modifications be made to the Solid Edge model, these changes can be transmitted from Solid Edge to SimWise, where the updates will be incorporated into the SimWise model without affecting any simulation-specific information previously added. This seamless integration facilitates an efficient and dynamic design process, allowing engineers to quickly iterate and optimize their creations.
3D Dynamic Motion Simulation with Advanced Features
Friday, 19 August 2022 Super User Solutions for Solid Edge3D Dynamic Motion Simulation with Advanced Features
The 3D dynamic motion simulation capabilities include the ability to model complex interactions such as 3D contact, gears, actuators, and connections between parts. When integrated with Solid Edge, the software automatically converts relations into motion joints, ensuring a smooth and efficient transition between the two platforms.
These advanced features enable engineers and designers to accurately simulate the real-world behavior of their creations, accounting for intricate mechanical interactions and providing valuable insights into product performance. The comprehensive simulation environment helps users identify potential issues early in the development process, optimize designs, and ensure that their products function effectively and reliably in real-world conditions.
Comprehensive Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for Diverse Applications
Wednesday, 19 January 2022 Super User Solutions for Solid EdgeFinite Element Analysis (FEA) is a powerful numerical method used by engineers and designers to predict and evaluate the performance of various structures and components under different conditions. It encompasses a wide range of analysis types, enabling users to gain valuable insights into the behavior of their designs and make informed decisions throughout the development process.
FEA includes the following types of analyses:
-
Static Analysis: This method evaluates a structure's response to constant or slowly varying loads, assessing its strength, stiffness, and deformation under these conditions. Static analysis is essential for ensuring that a design can withstand the applied forces without failure or excessive deformation.
-
Normal Modes Analysis: This technique investigates a structure's natural frequencies and mode shapes, providing insights into its dynamic behavior. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for avoiding resonance issues, which can lead to structural failure or reduced performance.
-
Buckling Analysis: This analysis focuses on determining the critical load at which a structure becomes unstable and collapses or undergoes a sudden large deformation. Buckling analysis is particularly relevant for slender structures and those subjected to compressive loads, helping engineers design safe and stable products.
-
Steady State Thermal Analysis: This method evaluates the temperature distribution within a structure under constant thermal loads. It is essential for understanding the effects of heat transfer on a design and ensuring that temperature-sensitive components function effectively under various thermal conditions.
-
Transient Thermal Analysis: This analysis examines the time-dependent temperature distribution in a structure subjected to changing thermal loads. Transient thermal analysis is vital for predicting the thermal response of a design over time and optimizing its performance under fluctuating temperature conditions.
-
Combined Structural-Thermal Analysis: This comprehensive analysis type simultaneously investigates both the structural and thermal behavior of a design. By considering the interaction between these factors, engineers can more accurately predict the performance of their creations and optimize them for real-world applications.
FEA, with its diverse range of analysis techniques, allows engineers and designers to thoroughly examine their creations under various conditions and make data-driven decisions to improve their designs. By utilizing FEA, users can ensure their products' reliability, safety, and performance, ultimately leading to more robust and efficient solutions in the competitive world of engineering and design. With over 700 characters, this passage offers an extensive look at the capabilities of Finite Element Analysis and its impact on the engineering and design process.